Instruments
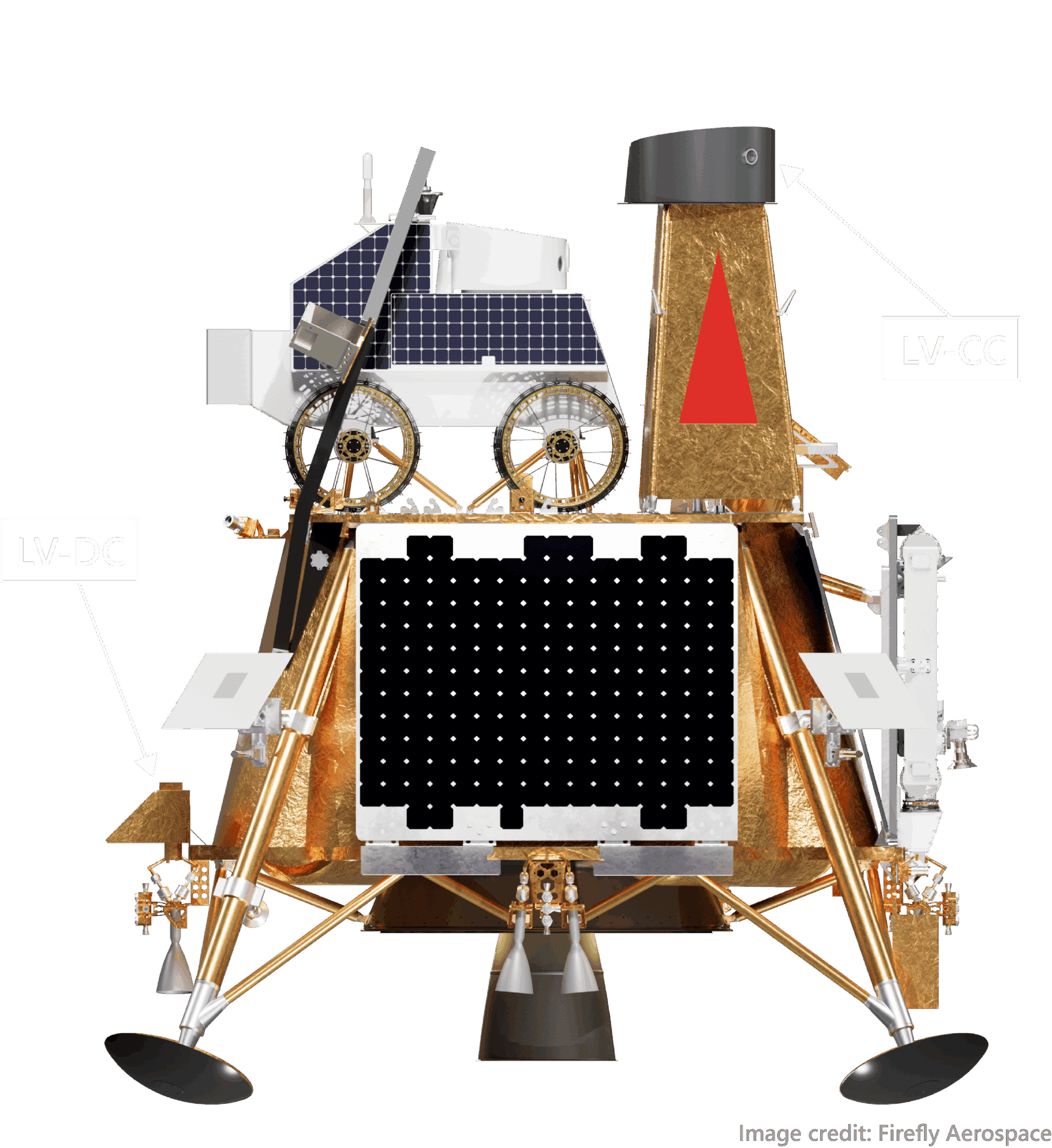
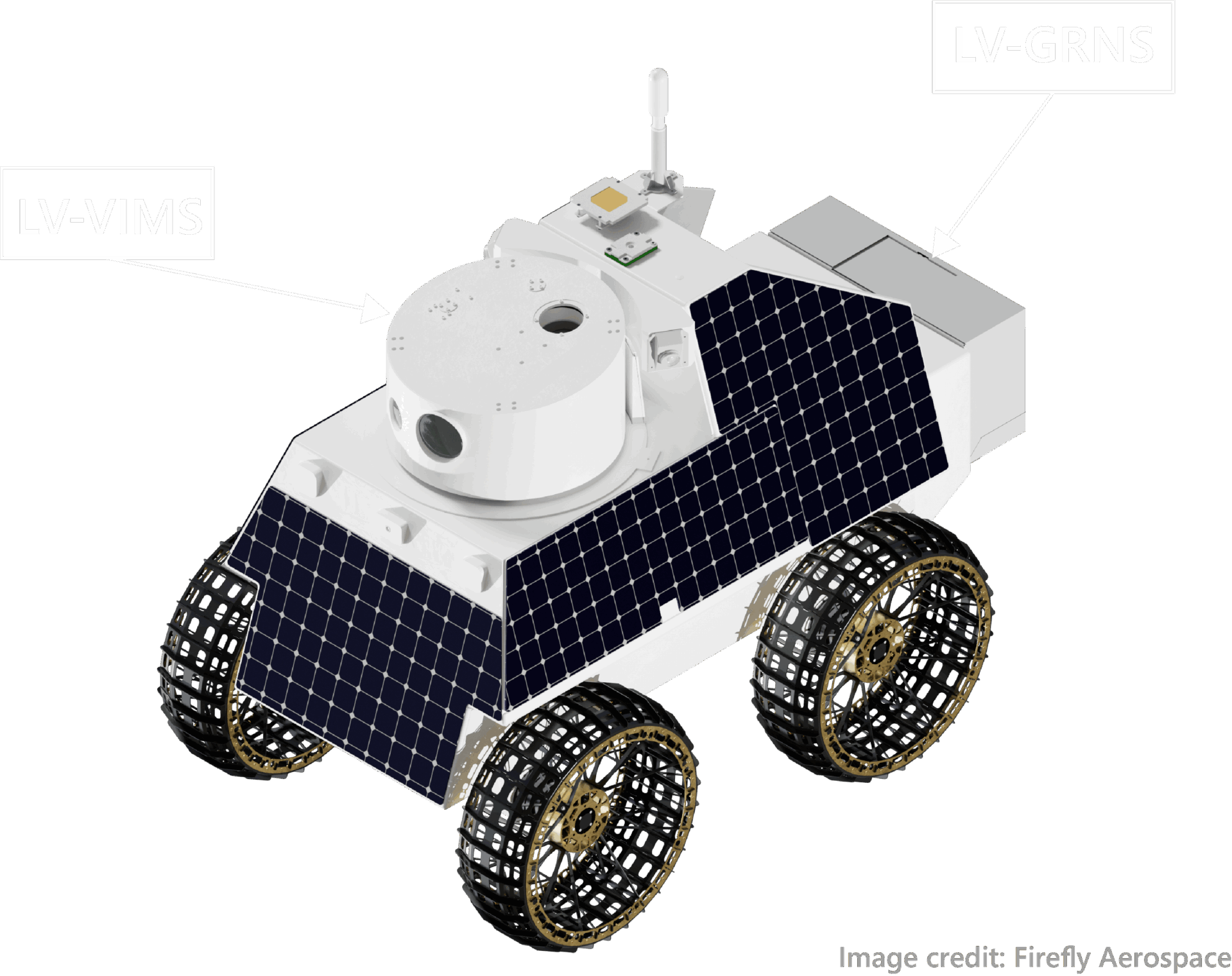
Notional Firefly Aerospace lander and Honeybee Robotics rover design.
Lander Payload
The Lunar-VISE lander suite has two cameras that will capture the descent to the Moon’s surface and image the area surrounding the landing site, including where the rover will traverse. Designed after the BAE Systems GeoSpace camera, both the Descent Camera (LV-DC) and Context Camera (LV-CC) have the ability to take images at a rate of up to five frames per second. The Descent Camera will be mounted on the lander and pointed at the lunar surface during landing, while the Context Camera will be placed on the top of the lander to make use of its capability to capture 270° panoramic scans of the landing site.
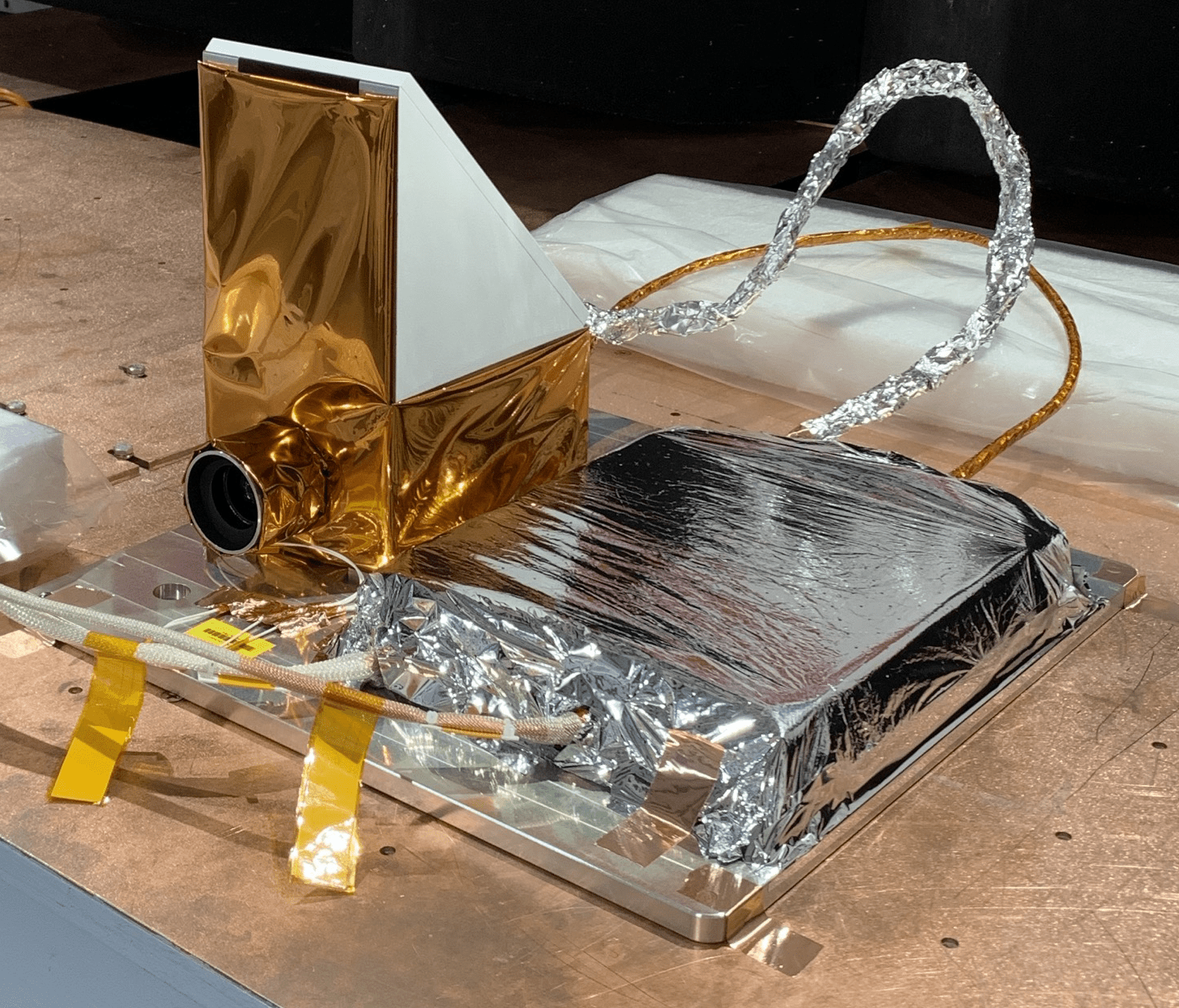
Lunar-VISE Descent Camera (LV-DC)
Key Measurements
- Geology of the greater area surrounding the landing site
- Regolith scoured from the surface and lofted during landing
- Time for regolith to settle
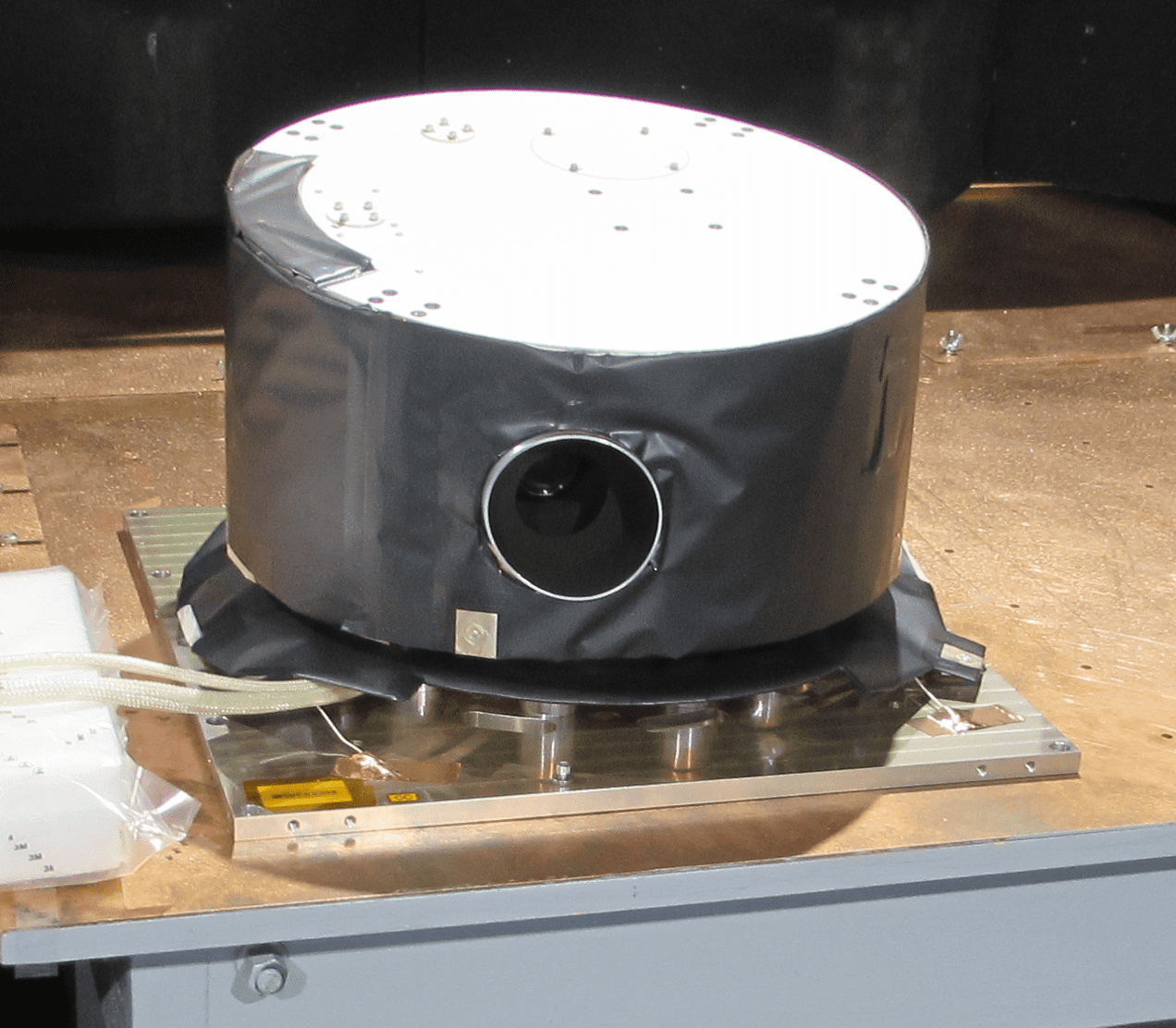
Lunar-VISE Context Camera (LV-CC)
Key Measurements
- Geology of the landing site throughout the lunar day
- Rover as it is traversing and conducting science investigation
- Regolith as it is disturbed by the rover traverse
Rover Payload
Lunar-VISE Visible/Infrared Multiband Suite (LV-VIMS)
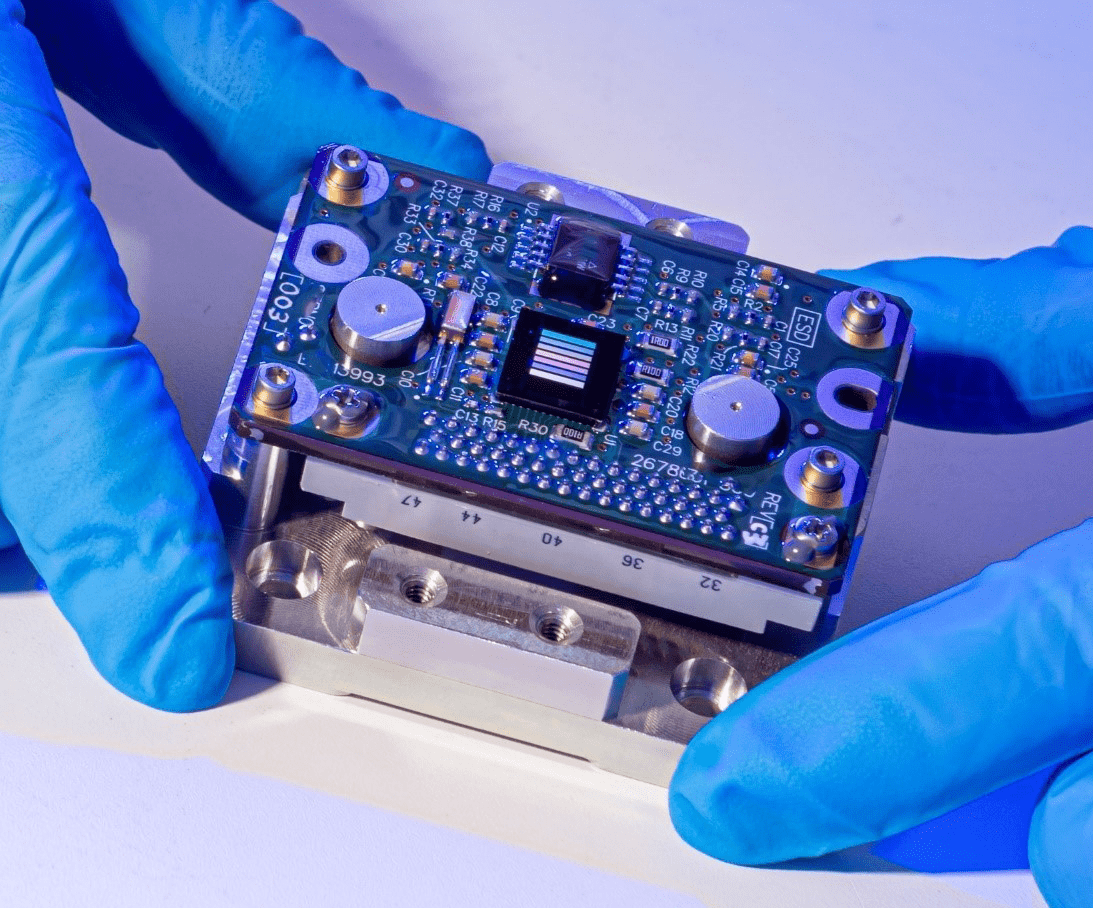
Lunar-VISE VNIR Imaging Camera (LV-VIC)
Visible to near-infrared (VNIR) Spectral Imaging
Key Measurements
- Composition of rocks and regolith making up the dome, particularly the abundance of Fe-bearing rocks and minerals
- Rock and regolith texture and morphology
Orbital Mission Comparisons
- Clementine Ultraviolet/Visible (UVVIS) camera
- Kaguya (SELENE) Multiband Imager (MI)
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Wide Angle Camera (LROC WAC)
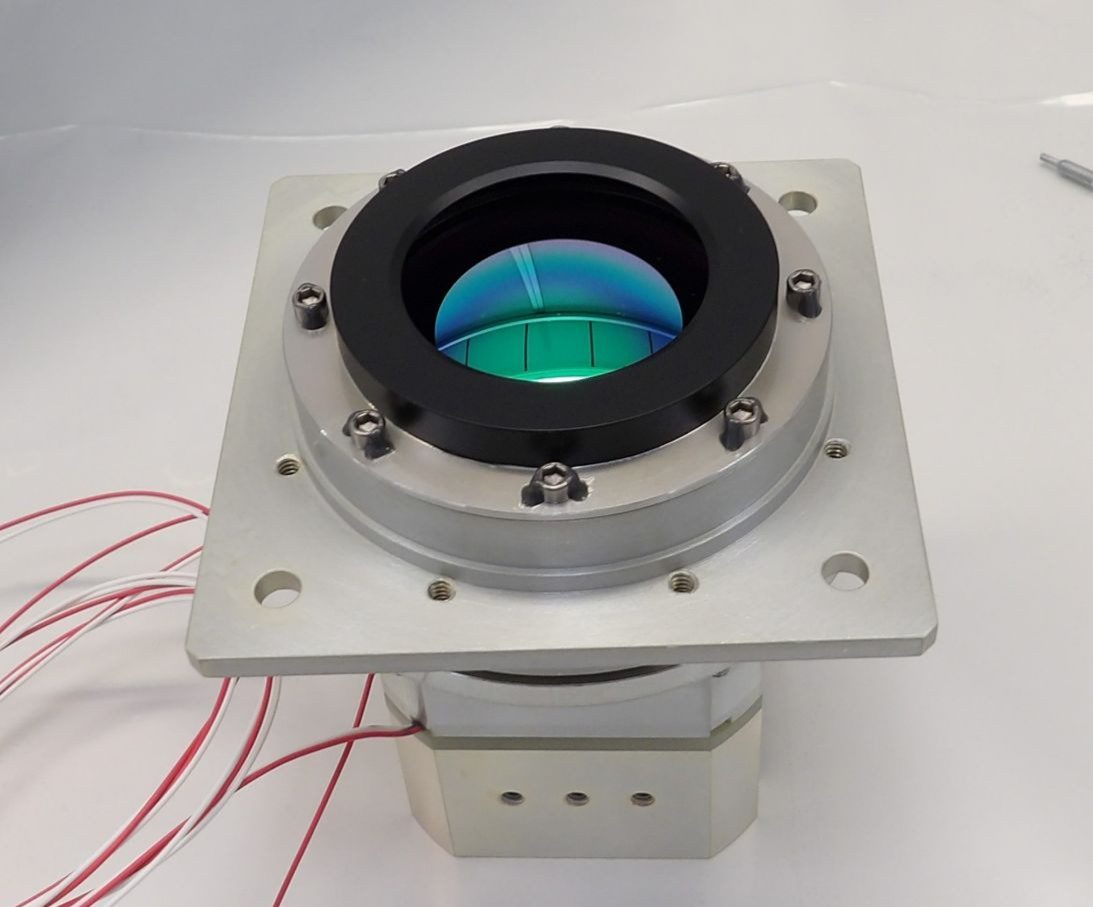
Lunar-VISE Compact Infrared Imaging System (LV-CIRiS)
Thermal Infrared Imaging Radiometer
Key Measurements
- Composition of rocks and regolith making up the dome, particularly the silica (SiO2) abundance
- Physical properties of the rocks and regolith including their thermal inertia and porosity
Orbital Mission Comparisons
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment
- Lunar Compact Infrared Imaging System (L-CIRiS on CP-22 as part of Intuitive Machines’ IM-4 mission)
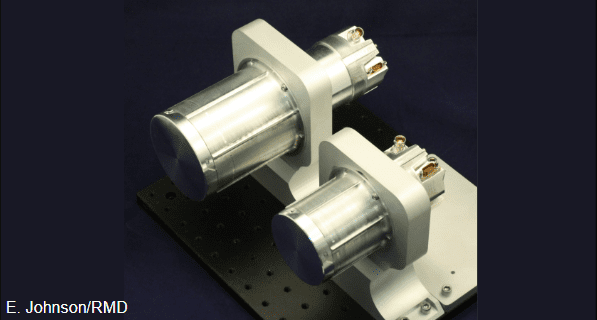
Lunar-VISE Gamma Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (LV-GRNS)
The LV-GRNS, built by Arizona State University and Radiation Monitoring Devices (RMD), has two sensor heads: the larger Gamma-Ray Sensor (GRS) and the smaller Neutron Sensor (NS). This novel two-detector system replaces the typical three minimum detector systems that are required to measure the same gamma-ray spectrum and two neutron energy ranges. The GRS is designed to maximize sensitivity to gamma rays while the NS primarily detects neutrons.
Gamma rays and neutrons are emitted from the lunar surface when radioactive isotopes (atoms with excess energy in its nucleus) decay and galactic cosmic rays hit the Moon.
Measuring the energy of these emissions can tell scientists about the surface’s elemental abundances.
The LV-GRNS measurements will provide key evidence and distinctions between different hypotheses for how silicic volcanism occurred on the Moon.